Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Dermatitis herpetiformis (DH) is a chronic, intensely itchy, blistering skin manifestation of gluten-sensitive enteropathy, commonly known as celiac disease. DH is a rash that affects about 10 percent of people with celiac disease.1 DH is found mainly in adults and is more common in men and people of northern European descent; DH is rarely found in African Americans and Asian Americans.2
Symptoms
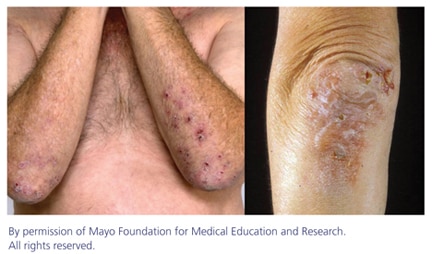
Dermatitis herpetiformis is characterized by small, clustered papules and vesicles that erupt symmetrically on the elbows, knees, buttocks, back, or scalp. The face and groin can also be involved. A burning sensation may precede lesion formation. Lesions are usually scratched off by the time a patient comes in for a physical exam, and the rash may appear as erosions and excoriations.
Patients with DH may also experience dental enamel defects to permanent teeth, which is another manifestation of celiac disease. Less than 20 percent of people with DH have symptoms of celiac disease.3
Causes
Dermatitis herpetiformis is caused by the deposit of immunoglobulin A (IgA) in the skin, which triggers further immunologic reactions resulting in lesion formation. DH is an external manifestation of an abnormal immune response to gluten, in which IgA antibodies form against the skin antigen epidermal transglutaminase.
Family studies show that 5 percent of first-degree relatives of a person with DH will also have DH. An additional 5 percent of first-degree relatives of a person with DH will have celiac disease.4 Various other autoimmune diseases are associated with DH, the most common being hypothyroidism.
Diagnosis
A skin biopsy is the first step in diagnosing DH. Direct immunofluorescence of clinically normal skin adjacent to a lesion shows granular IgA deposits in the upper dermis. Histology of lesional skin may show microabscesses containing neutrophils and eosinophils. However, histology may reveal only excoriation due to the intense itching that patients experience.
Blood tests for antiendomysial or anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies may also suggest celiac disease. Blood tests for epidermal transglutaminase antibodies are positive in more than 90 percent of cases.5 All of these tests will become negative with prolonged adherence to a gluten-free diet.
A positive biopsy and serology confirm DH and should be taken as indirect evidence of small bowel damage. A biopsy of the small bowel is usually not needed for DH diagnosis. However, if clinical signs of gastrointestinal disease are evident on examination, further workup may be required.2 Whether or not intestinal damage is evident, a gluten-free diet should be implemented because the rash of DH is gluten sensitive.4
Treatment
The sulfone dapsone can provide immediate relief of symptoms. For patients who cannot tolerate dapsone, sulfapyridine or sulfamethoxypyridazine may be used, although these medications are less effective than dapsone. A strict gluten-free diet is the only treatment for the underlying disease. Even with a gluten-free diet, medication therapy may need to be continued from a few months to 2 years.
DH can go into remission, which is defined as absence of skin lesions and symptoms of DH for more than 2 years while not taking sulfones or other treatments and not adhering to a gluten-free diet. Cohort studies showing DH remission provide support for reducing sulfone therapy and weaning from a gluten-free diet in patients with well-controlled DH.6
References
Clinical Trials
The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) and other components of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) conduct and support research into many diseases and conditions.
What are clinical trials, and are they right for you?
Clinical trials are part of clinical research and at the heart of all medical advances. Clinical trials look at new ways to prevent, detect, or treat disease. Researchers also use clinical trials to look at other aspects of care, such as improving the quality of life for people with chronic illnesses. Find out if clinical trials are right for you.
What clinical trials are open?
Clinical trials that are currently open and are recruiting can be viewed at ClinicalTrials.gov.
Alternate Versions
- PDF Version (PDF, 408 KB)
Additional Links
This content is provided as a service of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
(NIDDK), part of the National Institutes of Health. NIDDK translates and disseminates research findings to increase knowledge and understanding about health and disease among patients, health professionals, and the public. Content produced by NIDDK is carefully reviewed by NIDDK scientists and other experts.
The NIDDK would like to thank:
John J. Zone, M.D., University of Utah School of Medicine

