Definition & Facts of Bladder Infection in Adults
In this section:
- What is a bladder infection?
- Does bladder infection have another name?
- How common are bladder infections?
- Who is more likely to develop a bladder infection?
- What are the complications of a bladder infection?
What is a bladder infection?
A bladder infection is an illness most often caused by bacteria that enter your bladder and multiply. Bladder infections are the most common type of urinary tract infection (UTI). If untreated, bladder infections can spread to the kidneys and develop into a more serious infection.
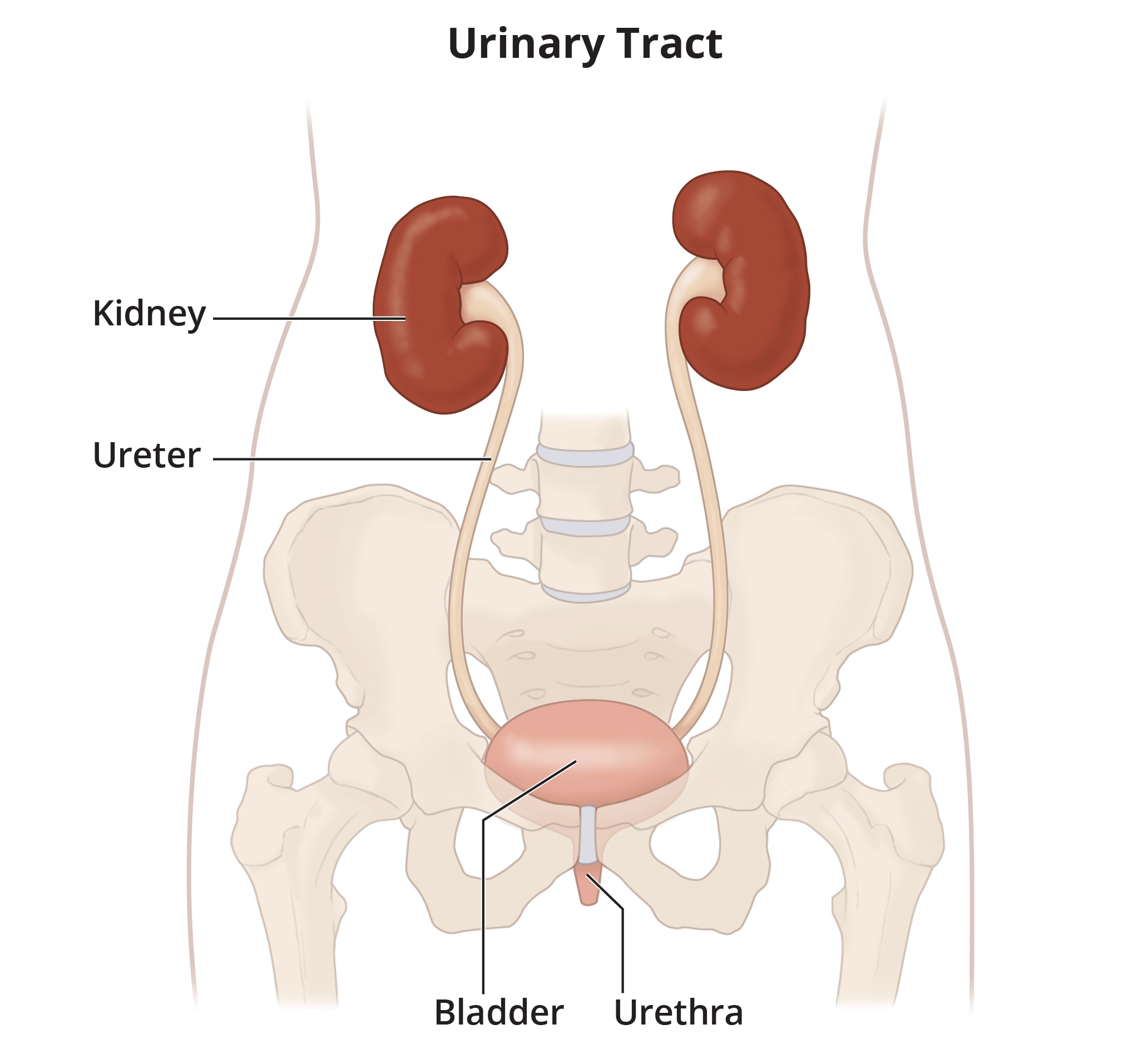 Bladder infections are the most common type of UTI.
Bladder infections are the most common type of UTI.Does bladder infection have another name?
Bladder infections may also be called cystitis. Sometimes people use the more general term, urinary tract infection or UTI, to mean a bladder infection. However, UTIs can occur in other parts of your urinary tract, including the urethra and kidneys.
How common are bladder infections?
Bladder infections are more common in women than in men.
Research shows that about half of all women will develop a bladder infection in their lifetime. About a quarter of those women will have repeat infections.1
Men under age 50 rarely get bladder infections.2
Who is more likely to develop a bladder infection?
Females are more likely to develop bladder infections than males due to their anatomy. Females have a short urethra located close to the anus, a source of bacteria. Therefore, bacteria from the anus may more easily enter the female urinary tract and cause a bladder infection. However, anyone with a bladder can develop a bladder infection, including children.
You are more likely to develop a bladder infection if you
- are sexually active or have gone through menopause
- use certain types of birth control, such as a diaphragm or spermicide
- had a UTI in the past
- have difficulty emptying your bladder completely
- use, or have recently used, a urinary catheter
- have a urinary tract blockage, such as a kidney stone or enlarged prostate
- have an abnormality in the urinary tract, such as vesicoureteral reflux
- have diabetes or problems with your immune system
What are the complications of a bladder infection?
When diagnosed early and treated properly, most bladder infections don’t lead to complications.
If untreated, a bladder infection can spread to one or both of your kidneys. Kidney infections are often very painful. Without treatment, kidney infections can cause serious health problems, such as permanent kidney damage.
Bladder infections that occur during pregnancy are more likely to spread to the kidneys. If you are pregnant, your health care professional may test your urine for bacteria. Regular testing can help your health care professional diagnose and treat a bladder infection before it leads to complications.
References
This content is provided as a service of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
(NIDDK), part of the National Institutes of Health. NIDDK translates and disseminates research findings to increase knowledge and understanding about health and disease among patients, health professionals, and the public. Content produced by NIDDK is carefully reviewed by NIDDK scientists and other experts.

